How To Create A Scenario Pivot Table Report In Excel
In this tutorial you will learn what a PivotTable is, find a number of examples showing how to create and use pivot tables in Excel 2016, 2013, 2010 and 2007.
Please Note, because this is a Microsoft Excel functionality, there would be a limit on the level of Support we would be able to provide with Troubleshooting.
If you are working with large data sets in Excel, pivot table comes in really handy as a quick way to make an interactive summary from many records. Among other things, it can automatically sort and filter different subsets of data, count totals, calculate average as well as create cross tabulations.
Another benefit of using pivot tables is that you can set up and change the structure of your summary table simply by dragging and dropping the source table's columns. This rotation or pivoting gave the feature its name.
- What is an Excel PivotTable?
- Creating a pivot table in Excel: quick start
- Using Excel pivot tables
- Pivot table examples
What is a pivot table in Excel?
An Excel PivotTable is a tool to explore and summarize large amounts of data, analyze related totals and present summary reports designed to:
- Present large amounts of data in a user-friendly way.
- Summarize data by categories and subcategories.
- Filter, group, sort and conditionally format different subsets of data so that you can focus on the most relevant information.
- Rotate rows to columns or columns to rows (which is called "pivoting") to view different summaries of the source data.
- Subtotal and aggregate numeric data in the spreadsheet.
- Expand or collapse the levels of data and drill down to see the details behind any total.
- Present concise and attractive online of your Excel data or printed reports.
For example, you may have hundreds of entries in your Excel worksheet with sales figures of local resellers:

One possible way to sum this long list of numbers by one or several conditions is to use Excel formulas as demonstrated in SUMIF and SUMIFS tutorials. However, if you want to compare several facts about each figure, using a pivot table is a far more efficient way. In just a few mouse clicks, you can get a resilient and easily customizable summary table that totals the numbers by any field you want.
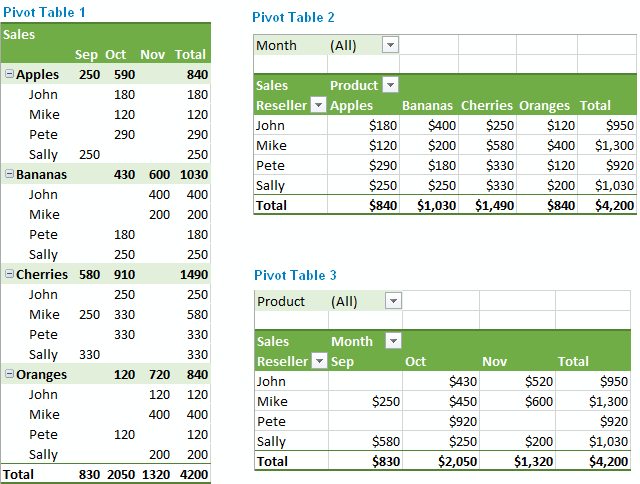
The screenshots above demonstrate just a few of many possible layouts. And the steps below show how you can quickly create your own pivot table in Excel 2016, 2013, 2010 and 2007.
How to make a pivot table in Excel: quick start
Many people think that creating an Excel pivot table is burdensome and time-consuming. But this is not true! Microsoft has been refining the technology for many years, and in the modern versions of Excel, the summary reports are user-friendly are incredibly fast. In fact, you can build your own summary table in just a couple of minutes. And here's how:
1. Organize your source data
Before creating a summary report, organize your data into rows and columns, and then convert your data range in to an Excel Table. To do this, select all of the data, go to theInsert tab and clickTable.
Using an Excel Table for the source data gives you a very nice benefit - your data range becomes "dynamic". In this context, a dynamic range means that your table will automatically expand and shrink as you add or remove entries, so won't have to worry that your pivot table is missing the latest data.
Useful tips:
- Add unique, meaningful headings to your columns, they will turn into the field names later.
- Make sure your source table contains no blank rows or columns, and no subtotals.
- To make it easier to maintain your table, you can name your source table by switching to theDesign tab and typing the name in theTable Name box the upper right corner of your worksheet.
2. Create a pivot table
Select any cell in the source data table, and then go to theInsert tab >Tables group >PivotTable.

This will open theCreate PivotTable window. Make sure the correct table or range of cells is highlighted in theTable/Range field. Then choose the target location for your Excel pivot table:
- SelectingNew Worksheet will place a table in a new worksheet starting at cell A1.
- SelectingExisting Worksheet will place your table at the specified location in an existing worksheet. In theLocation box, click the Collapse Dialog button to choose the first cell where you want to position your table.


Clicking OK creates a blank pivot table in the target location, which will look similar to this:

Useful tips:
- In most cases, it makse sense to place a pivot table in aseparate worksheet, this is especially recommended for beginners.
- If you are creating a pivot table from the data inanother worksheet or workbook, include the workbook and worksheet names using the following syntax [workbook_name]sheet_name!range, for example, [Book1.xlsx]Sheet1!$A$1:$E$20. Alternatively, you can click the Collapse Dialog button and select a table or range of cells in another workbook using the mouse.

- It might be useful to create apivot table andpivot chart at the same time. To do this, in Excel 2016 and Excel 2013, go to theInsert tab >Charts group, click the arrow below thePivotChart button, and then clickPivotChart & PivotTable. In Excel 2010 and 2007, click the arrow belowPivotTable, and then clickPivotChart.
3. Arranging the layout of your pivot table report
The area where you work with the fields of your summary report is calledPivotTable Field List. It is located in the right-hand part of the worksheet and divided into the header and body sections:
- TheField Section contains the names of the fields that you can add to your table. The filed names correspond to the column names of your source table.
- TheLayout Section contains theReport Filter area,Column Labels,Row Labels area, and theValues area. Here you can arrange and re-arrange the fields of your table.

The changes that you make in thePivotTable Field List are immediately reflected to your table.
How to add a field to Excel pivot table
Toadd a field to theLayout section, select the check box next to the field name in theFieldsection.

By default, Microsoft Excel adds the fields to theLayout section in the following way:
- Non-numeric fields are added to theRow Labels area;
- Numeric fields are added to theValues area;
- Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) date and time hierarchies are added to theColumn Labelsarea.
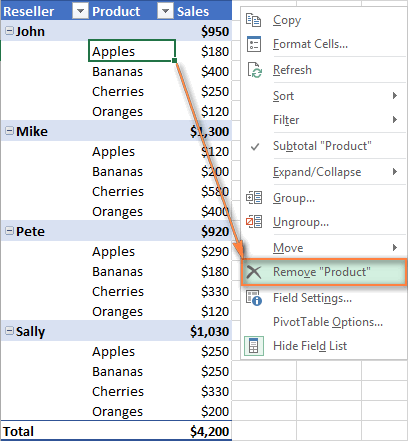
How to remove a field from a pivot table
To delete a certain field, you can either:
- Uncheck the box nest to the field's name in theField section of the PivotTable pane.
- Right-click on the field in your pivot table, and then click "Remove Field_Name".
How to arrange pivot table fields
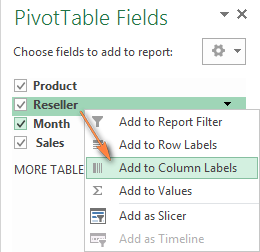
You can arrange the fields in theLayout section in three ways:
- Drag and drop fields between the 4 areas of theLayout section using the mouse. Alternatively, click and hold the field name in theField section, and then drag it to an area in theLayoutsection - this will remove the field from the current area in theLayout section and place it in the new area.

- Right-click the field name in theField section, and then select the area where you want to add it:
- Click on the filed in theLayout section to select it. This will also display the options available for that particular field.

4. Choose the function for the Values field (optional)
By default, Microsoft Excel uses theSum function for numeric value fields that you place in theValues area of the Field List. When you place non-numeric data (text, date, or Boolean) or blank values in theValues area, theCount function is applied.
But of course, you can choose a different summary function if you want to. In Excel 2016 an 2013, right-click the value field you want to change, clickSummarize Values By, and choose the summary function you want.
In Excel 2010 and lower, theSummarize Values By option is also available on the ribbon - on theOptions tab, in theCalculations group.
Below you can see an example of the pivot table with theAverage function:
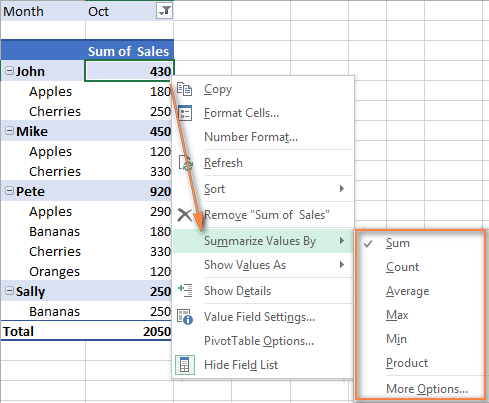
The functions' names are mostly self-explanatory:
- Sum - calculates the sum of the values.
- Count - counts the number of non-empty values (works as the COUNTA function).
- Average - calculates the average of the values.
- Max - finds the largest value.
- Min - finds the smallest value.
- Product - calculates the product of the values.
To get more specific functions, clickSummarize Values By >More Options… You can find the full list of available summary functions and their detailed descriptions here.
5. Show different calculations in value fields (optional)
Excel pivot tables provide one more useful feature that enables you to present values in different ways, for exampleshow totals as percentage orrank values from smallest to largest and vice versa. The full list of calculation options is available here.
This feature is calledShow Values As and it's accessible by right-clicking the field in the table in Excel 2016 and 2013. In Excel 2010 and lower, you can also find this option on theOptions tab, in theCalculations group.
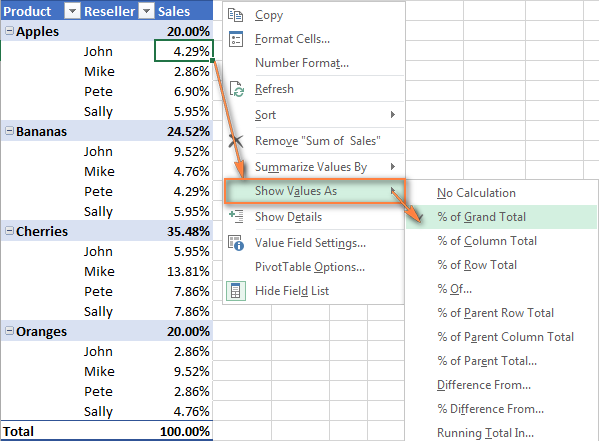
Tip. TheShow Values As feature may prove especially useful if you add the same field more than once and show, for example, total sales and sales as a percent of total at the same time. See an example of such a table.
This is how you create pivot tables in Excel. And now it's time for you to experiment with the fields a bit to choose the layout best suited for your data set.
Working with PivotTable Field List
The pivot table pane, which is formally calledPivotTable Field List, is the main tool that you use to arrange your summary table exactly the way you want. To make your work with the fields more comfortable, you may want to customize the pane to your liking.
Changing the Field List view
If you want to change how the sections are displayed in theField List, click theTools button, and choose your preferred layout.

You can alsoresize the pane horizontally by dragging the bar (splitter) that separates the pane from the worksheet.
Closing and opening the PivotTable pane
Closing thePivotTableField List is as easy as clicking theClose button (X) in the top right corner of the pane.Making it to show up again is not so obvious :)
To display the Field List again, right-click anywhere in the table, and then selectShow Field Listfrom the context menu.

You can also click theField List button on the Ribbon, which resides on theAnalyze / Options tab, in theShow group.

Using Recommended PivotTables in Excel 2016 and 2013
As you have just seen, creating a pivot table in Excel is easy. However, Microsoft Excel 2013 takes even a step further and proposes to automatically make a report most suited for your source data. All you have to do is 4 mouse clicks:
- Click any cell in your source range of cells or table.
- On theInsert tab, clickRecommended PivotTables. Microsoft Excel will immediately display a few layouts, based on your data.
- In theRecommended PivotTables dialog box, click a layout to see its preview.
- If you are happy with the preview, click the OK button, and get a pivot table added to a new worksheet.
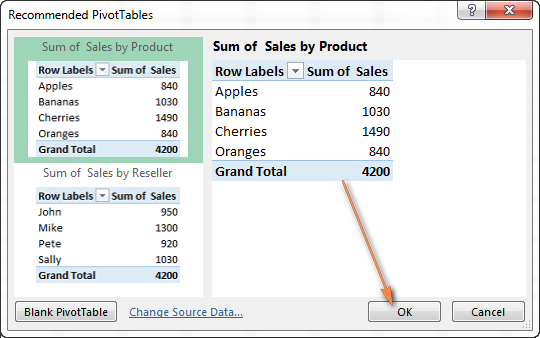
As you see in the screenshot above, Excel was able to suggest just a couple of basic layouts for my source data, which are far inferior to the pivot tables we created manually a moment ago. Of course, this is only my opinion and I am biased, you know : )
Overall, using the Recommended PivotTable in Excel is a quick way to get started, especially when you have a lot of data and are not sure where to start.
How to use pivot table in Excel
Now that you know the basics, you can navigate to theAnalyze andDesign tabs of thePivotTable Tools in Excel 2016 and 2013 (Options andDesign tabs in Excel 2010 and 2007) to explore the groups and options provided there. These tabs become available as soon as you click anywhere within your table.

You can also access options and features that are available for a specific element by right-clicking on it.
How to design and improve an Excel pivot table
Once you have created a pivot table based on your source data, you may want to refine it further to make powerful data analysis.
To improve the table's design, head over to theDesign tab where you will find plenty of pre-defined styles. To create your own style, click theMore button in thePivotTable Styles gallery, and then click "New PivotTable Style...".
To customize the layout of a certain field, click on that field, then click theField Settings button on theAnalyze tab in Excel 2016 and 2013 (Options tab in Excel 2010 and 2007). Alternatively, you can right click the field and chooseField Settings from the context menu.
The screenshot below demonstrate a new design and layout for our pivot table in Excel 2013.
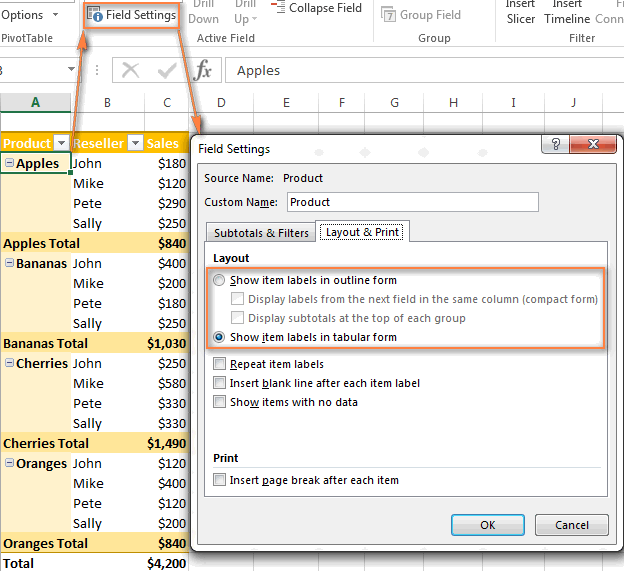
How to get rid of "Row Labels" and "Column Labels" headings
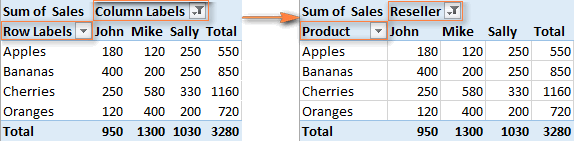
When you are creating a pivot table, Excel applies theCompact layout by default. This layout displays "Row Labels" and "Column Labels" as the table headings. Agree, these aren't very meaningful headings, especially for novices.
An easy way to get rid of these ridiculous headings is to switch from the Compact layout to Outline or Tabular. To do this, go to theDesign ribbon tab, click theReport Layout dropdown, and chooseShow in Outline Form orShow in Tabular Form.

This will display the actual field names, as you see in the table on the right, which makes much more sense.
Another solution is to go to theAnalyze (Options) tab, click theOptions button, switch to theDisplaytab and uncheck the "Display Field Captions and Filter Dropdowns" box. However, this will remove all field captions as well as filter dropdowns in your table.
How to refresh a pivot table in Excel
Although a pivot table report is connected to your source data, you might be surprised to know that Excel does not refresh it automatically. You can get any data updates by performing a refresh operation manually, or have it refresh automatically when you open the workbook.
Refresh the pivot table data manually
- Click anywhere in your table.
- On theAnalyze tab in Excel 2016 and 2013 (Options tab in earlier versions), in theData group, click theRefresh button, or pressALT+F5.
Alternatively, you can right-click the table, and chooseRefresh from the context menu.
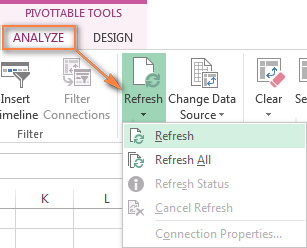
To refresh all pivot tables in your Excel workbook, click theRefresh button arrow, and then clickRefresh All.
Note. If the format of your pivot table gets changed after refreshing, make sure the "Autofit column width on update" and "Preserve cell formatting on update" options are selected. To check this, click theAnalyze(Options) tab >PivotTable group >Options button. In thePivotTable Optionsdialog box, switch to theLayout & Format tab and you will find these check boxes there.
After starting a refresh, you canreview the status orcancel it if you've changed your mind. Just click on theRefresh button arrow, and then click eitherRefresh Status orCancel Refresh.
Refreshing a pivot table automatically when opening the workbook
- On theAnalyze / Options tab, in thePivotTable group, clickOptions > Options.
- In thePivotTable Options dialog box, go to theData tab, and select theRefresh data when opening the file check box.

How to move a pivot table to a new location
If you want to move your table to a new workbook, worksheet are some other area in the current sheet, head over to theAnalyze tab in Excel 2016 and 2013 (Options tab in Excel 2010 and earlier) and click theMove PivotTable button in theActions group. Select a new destination and clickOK.

How to delete an Excel pivot table
If you no longer need a certain summary report, you can delete it in a number of ways.
- If your table resides in aseparate worksheet, simply delete that sheet.
- If your table is located along with some other data on a sheet, select the entire pivot table using the mouse and press theDelete key.
- Click anywhere in the pivot table that you want to delete, go to theAnalyze tab in Excel 2016 and 2013 (Options tab in Excel 2010 and earlier) >Actions group, click the little arrow below theSelectbutton, chooseEntire PivotTable, and then pressDelete.

Note. If any PivotTable chart is associated with your table, deleting the pivot table will turn it into a standard chart can no longer be pivoted or updated.
Pivot table examples
The screenshots below demonstrate a few possible pivot table layouts for the same source data that might help you to get started on the right path. Feel free to download them get a hands-on experience.
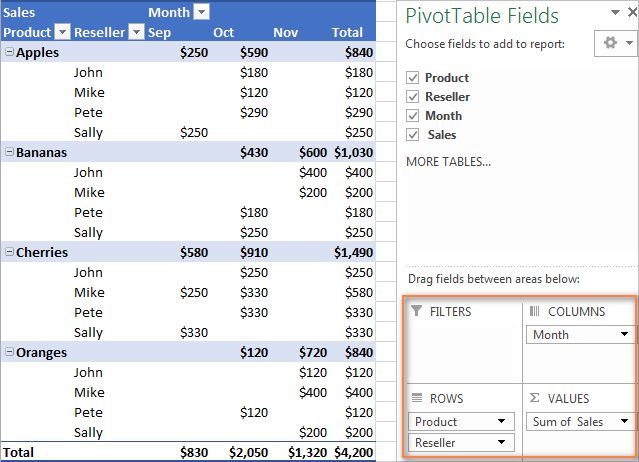
Pivot table example 1: Two-dimensional table
- No Filter
- Rows: Product, Reseller
- Columns: Months
- Values: Sales
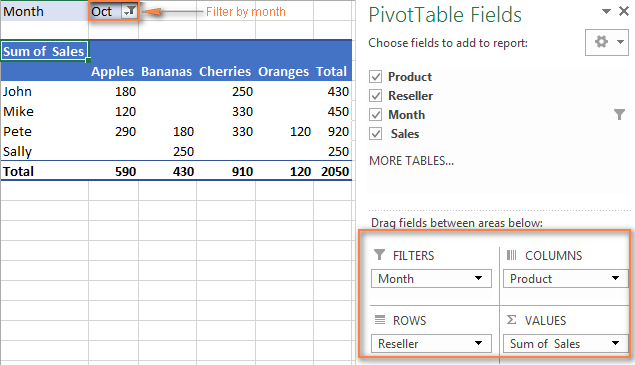
Pivot table example 2: Three-dimensional table
- Filter: Month
- Rows: Reseller
- Columns: Product
- Values: Sales
This pivot table lets you filter the report by month.
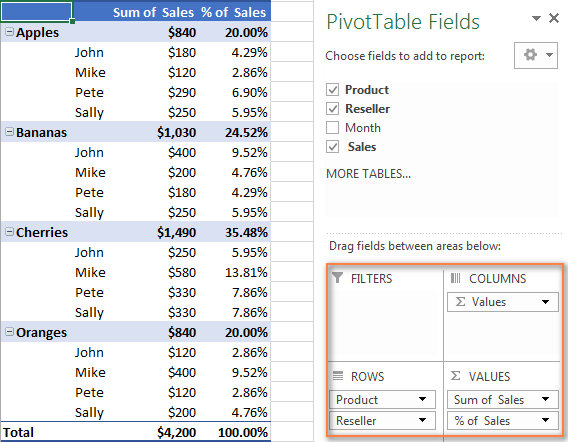
Pivot table example 3: One field is displayed twice - as total and % of total
- No Filter
- Rows: Product, Reseller
- Values: SUM of Sales, % of Sales
This summary report shows total sales and sales as a percent of total at the same time.
Available downloads:
- Pivot table examples
You may also be interested in:
- Tutorial - Basic Techniques for Filtering and Sorting Clio Exports in Excel
- Tutorial - Advanced Techniques for Filtering Clio Reports and Exports in Excel
How To Create A Scenario Pivot Table Report In Excel
Source: https://support.clio.com/hc/en-us/articles/360008354714-Tutorial-How-to-Use-a-PivotTable-to-Create-Custom-Reports-in-Microsoft-Excel
Posted by: hassourprive.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create A Scenario Pivot Table Report In Excel"
Post a Comment